Top 05 Oldest Countries in South Asia – A Historical Journey
South Asia is a region known for its rich cultural heritage and diverse history. It is home to some of the oldest civilizations in the world, with evidence of human settlements dating back thousands of years. In this article, we will take a journey through time and explore the top 05 oldest countries in South Asia.
1. India: The Cradle of Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization: The First Urban Culture
The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, is considered to be one of the oldest civilizations in the world. It flourished in the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE. The cities of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa were the major centers of this civilization, which had a highly advanced urban culture with well-planned streets, drainage systems, and public baths.
Vedic Period: The Birth of Hinduism
The Vedic period, which began around 1500 BCE, marked the beginning of Hinduism, one of the world’s oldest religions. The Vedas, the sacred texts of Hinduism, were composed during this period, and the caste system was established. The Vedic period also saw the rise of powerful kingdoms such as the Magadha and Maurya empires.
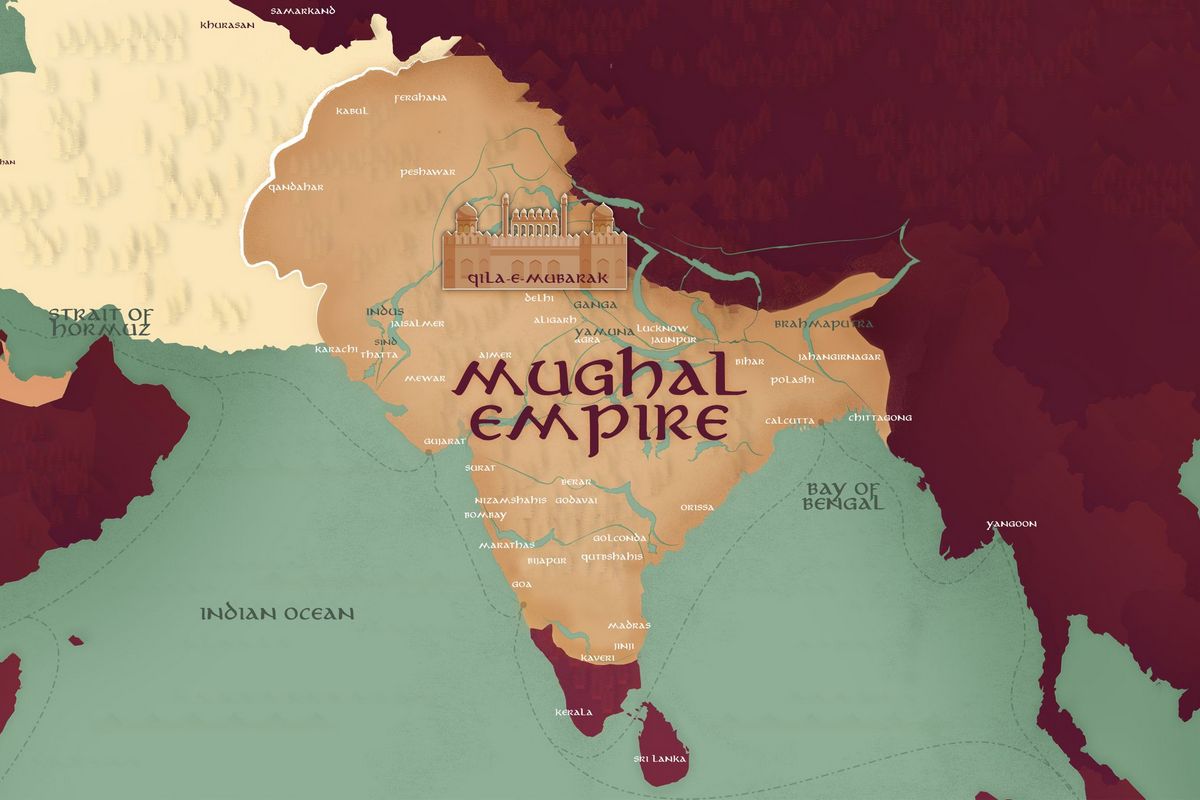
Mughal Empire: The Golden Age of India
The Mughal Empire, which ruled over most of the Indian subcontinent from the 16th to the 19th century, is considered to be the golden age of India. It was a period of great cultural, artistic, and architectural achievements, with the Taj Mahal being one of the most iconic structures built during this time.
2. Sri Lanka: The Land of Serendipity
Anuradhapura Kingdom: The First Capital
Sri Lanka, also known as the “Pearl of the Indian Ocean,” has a history dating back to over 3,000 years. The Anuradhapura Kingdom, which was established in the 4th century BCE, is considered to be the first major kingdom in Sri Lanka. It was a center of Buddhism and saw the construction of magnificent structures such as the Ruwanwelisaya stupa.
Polonnaruwa Kingdom: The Golden Age
The Polonnaruwa Kingdom, which succeeded the Anuradhapura Kingdom, is known as the golden age of Sri Lanka. It was a period of great prosperity and cultural achievements, with the construction of impressive structures such as the Gal Vihara statues.
Colonial Rule: The Portuguese, Dutch, and British Influence
Sri Lanka was colonized by the Portuguese, Dutch, and British in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries respectively. These colonial powers left a lasting impact on the country’s culture, architecture, and language. Sri Lanka gained independence from British rule in 1948.
3. Nepal: The Land of Mount Everest
Licchavi Dynasty: The First Rulers
Nepal, a landlocked country situated in the Himalayas, has a history dating back to the 6th century BCE. The Licchavi dynasty, which ruled from the 3rd to the 9th century CE, is considered to be the first rulers of Nepal. They were known for their patronage of Buddhism and the construction of magnificent temples and palaces.
Malla Dynasty: The Golden Age
The Malla dynasty, which succeeded the Licchavis, is known as the golden age of Nepal. It was a period of great cultural and artistic achievements, with the construction of impressive structures such as the Pashupatinath Temple and the Bhaktapur Durbar Square.
Unification under Prithvi Narayan Shah
In the 18th century, Nepal was divided into several small kingdoms. It was under the rule of King Prithvi Narayan Shah that these kingdoms were united, and modern-day Nepal was formed. He is considered to be the founder of the Kingdom of Nepal.
4. Bangladesh: The Land of Bengal
Ancient Kingdoms: Pundra, Vanga, and Samatata
Bangladesh, a country situated in the fertile Ganges delta, has a history dating back to over 3,000 years. It was home to ancient kingdoms such as Pundra, Vanga, and Samatata, which flourished from the 6th century BCE to the 11th century CE.
Mughal Rule: Influence on Culture and Architecture
Bangladesh was under Mughal rule from the 16th to the 18th century. This period saw the spread of Islam and the construction of magnificent structures such as the Lalbagh Fort and the Sixty Dome Mosque.
Independence from British Rule
Bangladesh gained independence from British rule in 1947, along with India and Pakistan. However, it was not until 1971 that Bangladesh became an independent nation after a bloody war of independence with Pakistan.
5. Bhutan: The Land of the Thunder Dragon
Pre-Buddhist Era: The Bon Religion
Bhutan, a small landlocked country nestled in the Himalayas, has a history dating back to the pre-Buddhist era. The Bon religion was the dominant faith during this time, and many ancient temples and monasteries were built.
Buddhism: The State Religion
Buddhism was introduced to Bhutan in the 7th century, and it became the state religion in the 8th century. The country is known for its numerous monasteries and temples, including the famous Taktsang Monastery, also known as the Tiger’s Nest.
Unification under Zhabdrung Ngawang Namgyal
In the 17th century, Bhutan was divided into several small kingdoms. It was under the leadership of Zhabdrung Ngawang Namgyal that these kingdoms were unified, and modern-day Bhutan was formed. He is considered to be the father of Bhutan.
FAQs
What is the oldest country in South Asia?
India is considered to be the oldest country in South Asia, with a history dating back to over 5,000 years.
Which country in South Asia has the most ancient civilization?
The Indus Valley Civilization, which flourished in present-day India and Pakistan, is considered to be the most ancient civilization in South Asia.
What is the oldest religion in South Asia?
Hinduism is the oldest religion in South Asia, with roots dating back to the Vedic period in ancient India.
Which country in South Asia has the most UNESCO World Heritage Sites?
India has the most UNESCO World Heritage Sites in South Asia, with 38 sites recognized by UNESCO.
What is the significance of the Mughal Empire in South Asia’s history?
The Mughal Empire, which ruled over most of South Asia from the 16th to the 19th century, is considered to be the golden age of the region. It left a lasting impact on the culture, architecture, and language of South Asia.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of History and Culture
South Asia is a region steeped in history and culture, with each country having its unique story to tell. From the ancient Indus Valley Civilization to the golden age of the Mughal Empire, these countries have witnessed the rise and fall of powerful dynasties, the spread of religions, and the influence of colonial powers. As we take a journey through time, we can see how these countries have evolved and shaped the rich tapestry of South Asian history and culture.
Recent Posts
How many days are ideal for Laos?
How many days are ideal for Cambodia?
Hanoi vs Bangkok: Where is safer?
All Categories

Thailand




